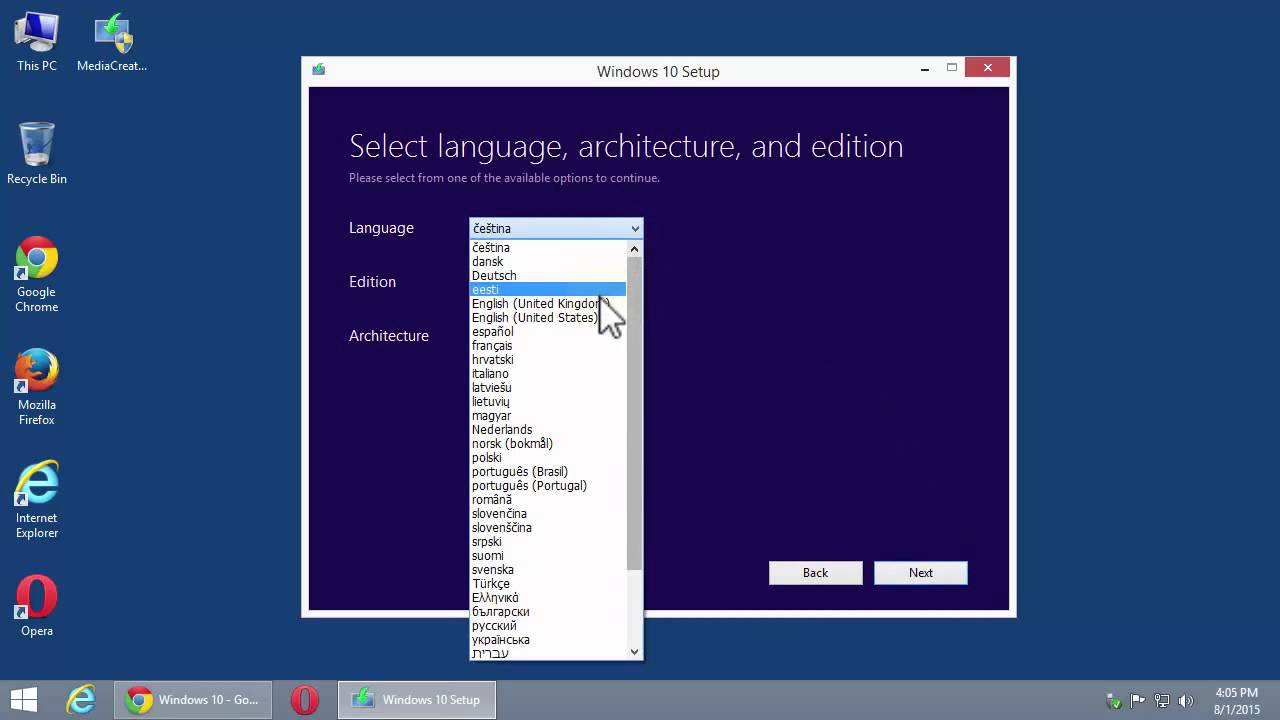
Step 1. Create a new ISO image file:
- A blank USB flash drive with at least 5 GB of space or blank DVD (and DVD burner) if you want to create media. We recommend using a blank USB or blank DVD, because any content on it will be deleted. When burning a DVD from an ISO file, if you are told the disc image file is too large you will need to use Dual Layer (DL) DVD Media.
- Locate the.iso file that you want to use. Double click the file. Alternatively, you can right-click the file and choose Mount from the menu. After the disk image is mounted you should see a new disk available in This PC.
- Imaging is a way of backing up the computer that allows you to store the entire computer, including the operating system and programs, in a single file (an 'image') that can be used to restore the computer to exactly the way it was when the image was made. This is a good way to recover from major hardware failure without having to spend lots of time reinstalling programs, restoring data, etc.
To create toolbar button, or choose File > Create ISO Image > Create ISO Image command
To import some files and folders to a newly created ISO: click Import ISO image toolbar button, or choose a related command from the menu. Add existing folder to a new ISO image
Step 2: Add more data to ISO image file:
Select a folder in a file tree where you want data to be added
Click Add File toolbar button or a related command from the Edit menu to add a file or group of files
Click Add Folder toolbar button or a related command from the Edit menu, or press Insert key to add a folder
If you want a new custom folder to be created inside ISO's file tree, click Create new folder toolbar button, or choose a related command from the Edit menu, or from the context menu. Enter the name of the folder and click Create button
Drag'n'Drop files and folder from the Windows Explorer to the place within ISO's file tree to add them to ISO
This suggests an excellent, free program to use and how to extract an ISO / Disk Image File using that program to the Windows desktop, or wherever you like, for use in any number of situations. First you will need to download and then install this program from the link below. To create the disk image, you'll need an external USB drive to connect to your Raspberry Pi and write it to. If the USB drive is a higher capacity than the source microSD card (ex: a 32GB USB drive.
Step 3: Specify ISO label and boot options:
How To Make Disk Image File
At bottom of the working area type a label for the CD/DVD/Blu-ray which will be displayed in Windows Explorer and CD/DVD/Blu-ray drive properties
To make an ISO bootable, click Add Boot Image checkbox and specify emulation type (Floppy 1.2MB, 1.44MB, 2.88MB or HDD) and boot image to be added to boot area
Step 4: Compile and save the ISO Image:
Click the Save ISO image toolbar button, or choose a related command from the File menu, or press Ctrl+S
Choose a name and location for the ISO image file to be created and click Save
Wait while the ISO image being compiled. You can see the progress and click the Cancel button to cancel the ISO image compilation process
How to create an ISO Image from a CD/DVD/Blu-ray Disc
Click Make ISO from CD/DVD/Blu-ray toolbar button, or choose a related Select a source CD/DVD/Blu-ray reader/writer device where you inserted a data CD/DVD/Blu-ray disc
Select a target ISO image file name and path and click
Select a target ISO image file name and path and click Make
- Wait while the ISO image being created. You can see the progress and click the Cancel button to cancel the ISO image creation process
Create a Disk Image
A Disk Image is a mirror copy of your entire logical drive (volume) or physical device (HDD, USB, ...) stored as set of files. It may be agood idea to create a Disk Image for a drive containing deleted files that you want to recover,if you have enough space on another drive.
You might ask, 'Why should I create a Disk Image on a drive that holds my deleted files?'
Here is the answer: If you do something wrong while attempting to recover the files (for example, recovering files onto the same drive could destroy their contents), you will be able to recover these deleted files and folders from the Disk Image that you have wisely created.
How To Make Disk Image File
Disk Image (Active@ Image format) consists of configuration file (with an extension .DIM) and set of file chunks having extensions .000, .001, .002 ... By default Active@ File Recovery tries to create one file (chunk) for the whole volume/device. However, if the target location is FAT, it may not be possible due to file system limitations. In this particular case the disk image is split into several chunks and each file has a size of 2Gb. Chunks content can be RAW or RAW-Compressed, depending on settings.
To create a Disk Image:
- Start Active@ File Recovery and select a drive (volume) or physical device that you want to create image for
- To open the Create Image dialog box, do one of the following:
- Choose Create Image... from the File menu
- Press Ctrl+I key combination
- Right-click the device and choose Create Image on the context menu
- Select another physical device or another logical drive to store Disk Image files
- Browse to the folder where you want to save the Disk Image
- To give the Disk Image file a different name, type a new name in the File Name field
- Click Save to start Disk Image creation
- Watch the progress and wait while drive's contents are copied to the new location. You may cancel the process of image creation anytime by clicking Stop
To create Disk Image default options being used.
To change Disk Imaging default options:
- Click Settings toolbar button, or choose Settings... from View menu, or press F2
- Click Images tab
- Change default storage path, locking and error options, compression and chunks splitting options:
Important
You must always create a Disk Image on a drive other than the source drive. Do not try to save a Disk Image of a drive onto itself.
